Keywords:mining groundwater,resource quantity,protection method,system.
Abstract
During the development of mining proj-ccts,it is casy for sewage to lcak or spills to occur.If these pollutants enter groundwater,theself-cleaning cycle is long,or the sphere of influ-ence is large,the productive activities and lives ofpeople will be significantly affected.Therefore,aseries of protective measures making up a targetedapproach to protecting groundwater quantity isnecessary.This article explores four approaches tocomprehensive measures for protecting groundwa-ter quantity and summarizes the proposed ground-water-quantity protection process,which is gov-erned by the following guiding principles:miningoptimization,block plugging,pillar protection,andrecycling.
Introduction
The first upsurge of groundwater environmentalquality assessment took place in Western devel-oped countries in the 1950s and 1960s.China’sfirst groundwater pollution survey and assessmentwork can be traced back to the 1970s at the earli-est.At that time,mainly inorganic tests were car-ried out,but the tcchncal level was lower.Chinadid not carry out specially focused groundwaterpollution investigation work until the 1990s.Atpresent,survey data on groundwater pollution inChina are still inadequate,and the overall pollutionsituation country-wide is still unclear.The impactof groundwater contamination,its spatial and tem-poral distribution characteristics,and its transportproperties are still not well understood.
In recent years,some researchers have carried outuseful investigations involving quantitative study ofthe impact of human activities on the water cycle.Methods have included the earth dynamicsmethod,artificial neural networks using the defaultfactor method,the variation coefficient method,theprojection pursuit regression model,and theweighted index method,all of which have played animportant role in advancing the study of groundwa-ter.This article,on the basis of previous researchcombined with concrete and practical findings,hasproposed an effective method for controlling con-tamination of groundwater by mine developmentprojects and concludes with an eight-word policyfor groundwater protection.
Optimizing mining and reducing groundwaterloss
To avoid surface subsidence and dislocation,reduce surface deformation,protect farmland andbuildings,refrain from damaging undergroundaquifers,and prevent large-scale groundwaterinflux underground,mining methods should opti-mized.Currently,advanced mining methods con-sist of cemented backfill mining technology,large-spacing centralized sublevel caving miningtechnology,hanging-wall ore-mining technology,various mining methods using residual ore-ex-traction technology and others.In this paper,forthe Da Jia Zhuang Iron Mine which was the objectof thisresearch,the stage subsequent-filing emp-ty-field method was the protection method best suited to their characteristics
The stage subsequent-filling empty-field methodhas been successfully used in many mines aroundthe world.At present,iron mines in China whichuse subsequent-filling mining methods include theCaolou and Lilou iron mines in the Anhui Huoqiuregion,the Mazhangtun iron mine,the Jinling ironmine,the Mazhuang and Gujiatai iron mines inShandong,and the Baoshan iron mine in Xinjiang.Currently,Chinese filling mining technology iscoming to be used in deep mining,for example inthe Fankou and Huize lead-zinc mines and the Da-hongshan and Dongguashan copper mines,thusplaying a huge role in deep resource exploration[1,2].Currently,filling mining methods have beenwidely used in Chinese nonferrous mines,and theproportion of ferrous and coal mines using thistechnology is increasing year by year.In othercountries,the Mount Ai copper mine in Australia,the Tara lead-zinc mine in Ireland,the New BrokenHill mine in Canada,the Clayton copper-nickelmine in South Africa,the Jiayin copper mine inRussia,and the Lubiersi copper-lead mine in Spainare using this technology in the mining process,and most of these involve deep mining.
Mine excavation uses filling mining technology;de-pending on mining capacity and filling ability andmeans,filling technology uses vertical sand binsand a barrel mixing process.Stage filling is used instope filing.To avoid slurry leakage accidents [3,4],the pressure on the walls caused by the filling bodymust be reduced,first by filling 6 meters withhigh-ratio filling material,then sequentially fillingstep by step until the stope is full.The body mainte-nance time for mining-block filling for steps 1 and 2is three to four months.
In addition,measures which ensure proper con-trol of the exploitation and exploration range mustbe carried out to protect groundwater resources.According to the principle of minimal impact ongroundwater,the mine which has less impact on
groundwater should be exploited first.In cases ofoverexploitation of groundwater mining areas,ifmining continue to affect drainage and groundwa-ter,mining should be restricted or prohibited.
Combining grouting with anchoring and shot-creting to stop water breakouts undergroundOre bodies occur in rock strata and have a certaineffect on drainage for bedrock above the mininglevel.The main water supply source for areagroundwater was quaternary water,and thereforeprotecting this quaternary water from loss was veryimportant.The two main ways to deal with highgroundwater pressure are water drainage andwater plugging.However,drainage easily leads towater disasters of different levels of severity and re-duces groundwater resources,thus affecting theproductive and life activities of local people.There-fore,blockage approaches are more and more usedto solve groundwater problems [5,6].Water plug-ging by dynamic water grouting is recommend.Inthe case where water bursts in at a water breakoutpoint,grouting to seal this water breakout point isused.The approach used is “resistance up,inter-cept middle,block down”to form a three-dimen-sional water-plugging pattern.A diagram of thegrouting process is shown in Figure 1.
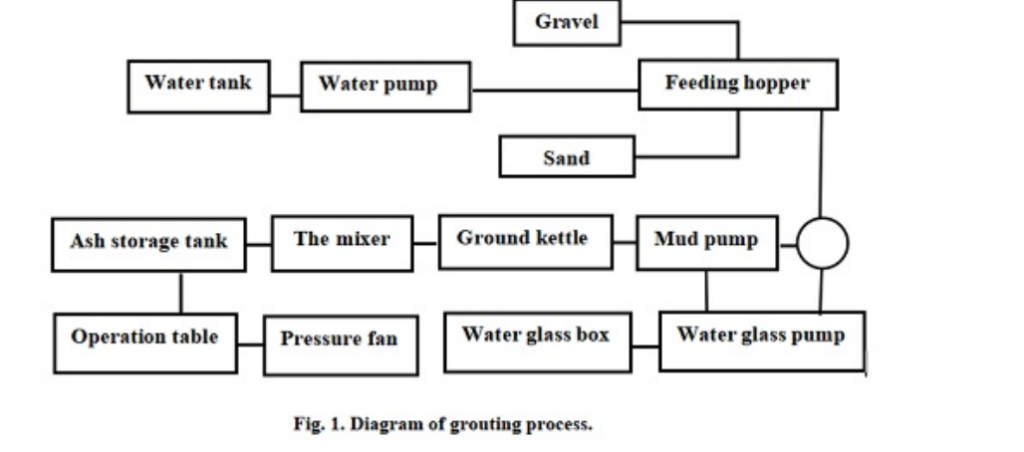
In the process of mining Dajiazhuang iron ore,certain measures can be generally used to resistwater,such as working-face pregrouting,groutingbehind segments,injecting grout in separatelayers,and dynamic water grouting.In the aquifer,cement guniting is used for shield-wall blocking.Inlocal faults,anchoring and shotcreting are combined with guniting to block off water.During prac-tical production,mine-water inflow observationshould be strengthened.According to the regula-tions for prevention and control of coal-mine wateras compiled by the State Administration of CoalMine Safety [8],mine operations should adhere tothe principles of“Prediction and forecast,explorewhen there is doubt,excavating after exploration,treatment before exploiting”and should take com-prehensive measures for prevention,plugging,dredging,draining,and cutting off.Reliable water-proofing measures should be implemented beforeallowing excavation.
In possible aquifer areas,the shaft freezingmethod should be used to reduce the possibility ofchange in rock-mass mechanical properties andwater drainage into the aquifer.Exposed aquifershould be plugged in a timely manner during con-struction.The construction sequence should be ar-ranged reasonably.Before the end of working-facepreparation,the underground mine-water recyclingsystem should have been constructed and verified
Waterproof pillars to reduce the influence ofgroundwater
To reduce the influence of weathering fissure-wa-ter aquifers such as strong quaternary system aqui-fers through the contact zone to the mining pit,acertain thickness of cap pillar should be reservedunder the bedrock weathering zone during mining.For protection of quaternary groundwate,farm-land,and architectural structures,bodies of ironore above -150m(-120 m to 150 m)can be usedas a top pillar because ore bodies above -150 mare not within the scope of mining;this can greatlyreduce the influence on the surface after iron-oremining.
During mining operations,mining and fillingshould be carried out according to the optimizeddesign parameters.Goaf should be filled withoutdelay,and the appropriate filling coefficient andstrength requirements should be ensured.The nec-essary protection pllars should be set aside to
guarantee the overburden and stability of the sur-rounding rock without caving,which will protectsurface stability..
Reinjection of mine water to recover water quan-tity
One very good approach to protecting groundwa-ter resources is to recycle the iron-ore mine watercompletely,thus avoiding new exploitation ofgroundwater.At present,some management tendsto propose a requirement for complete and compre-hensive reuse of mine water.In terms of groundwa-ter,such a requirement would be positive and bene-ficial.However,one size does not fit all in terms ofsystem policy.The water inflow is very big in manymines,and the potential for recycling is not much.In the northern winter,the mines cannot supportirrigation,and comprehensive reuse becomes com-pletely impractical.Among all the recycling condi-tions that the mine encounters,the response of ab-normal conditions should be considered.For exam-ple,users may transfer the mine water they receive,reduce their demand,or no longer need water.Insome local mining areas,the volume of mine wateris too large to reuse,and the proper handling anduse of mine water should be considered.Studieshave suggested the purification of excess minewater back into nature,where it will take part ingroundwater,surface water,the evaporation cycle,and atmospheric precipitation,while also playing arole in recovering the ecological environment.Re-turning mine water into natural cycles also pro-vides good protection of groundwater resources [7].
Two main factors must be considered with rein-jection:area and timing.In choosing a reinjectionarea,the best option is an independent closed aqui-fer no far from the mining area.This does not affectmining safety and provides the benefit to the aqui-fer of having a significant water supply.As for rein-jection timing,an independent aquifer at the end ofthe seam mining period can be chosen.Providedthat this does not affect mining safety,the minewater is reinjected into the main aquifer.In this case,this is a quaternary system aquifer of sub-stantial water-supply significance,which offers agood way to protect and restore groundwater re-sources.Now there are many application examplesin inland areas.The Wutongzhuang mine-water re-injection project is a good example.
In this research,the advanced technology oftube-well injection was considered suitable formine-water injection in the Dajiazhuang iron-oremine.This approach recharges the purifica-tion-treatment mine water to the aquifer.A reinjec-tion project must forecast the flow field,performearly detection,and avoid water inrush.Safetyshould be a primary considerationin protectinggroundwater resources.The reinjection layerrshould be located in a horizon which has enoughstorage space,does not have blowby up or down,and has good lateral connectivity.In addition,in-jection should not have a bad effect on drink-ing-water sources.Furthermore,the reinjectionwater must have good compatibility with reinjec-tion-layer lithology and strata and must not formsecondary precipitation which clogs the underlyinglayer.
Summary
Based on the research into groundwater protec-tion methods described in this paper,the authorssuggest that,for mine development projects,opti-mal mining should combine pulp and anchorspray-seal plugging,the retention of reinforcing pil-lars,and appropriate retention methods for minewater.summary above The water-resource vol-ume-protection method can be summarized as“mining optimization,block plugging,pillar pro-tection,and recycling”,which is an eight-wordstatement of a groundwater-protection policy.Thisresearch could provide a reference for similar con-struction and development projects involving pro-tection of groundwater volume.
References
[1]X.Y.Wang,M.S.Wang.Mountain tunnel waterlimited plugging drainage study on external waterpressure on lining,J.Chinese Journal of geotech-nical engineering,27(2005):125-127.
[2]J.X.Zhang,X.H.Ren,H.D.Jiang,L.W.Huang.Un-der high external water pressure study on seepagecontrol measures of tunnel engineerin,J.Hydroge-ology and engineering geology 6(2006),62.
[3]Zhukun,Chenhui,LiGuangHe,etal.In-Situ Re-mediation of Petroleum Compounds in Groudnwa-ter A quifer With Chlorine Dioxide[J].WatRes,1998,32(5):1471-1480.
[4]Kao CM,Lei SE.Using a Peat Biobarrier to Re-mediate PCEP TCE Contaminated Aquifer[J].WatRes,2000,34(3):835-845.
[5]S.Y.Lee King of dynamic water Grouting tech-nique blocked mine water inrush,J.Coal scienceand technology 2000(8),28(8):28-30.
[6]E.W.E,Z.H.Meng.Complex flood deposits safeminingtechnologyresearchMetalmines,2006(12):7-10.
[7]Gang Liang.The Current Situation and Interac-tion Mechanism Research of Coal Mine’s EIA andEnvironmental Acceptance.The 2nd InternationalConference on Artificial Intelligence,ManagementScience and Electronic Commerce (AIM-SEC),2011,Volume3,PartⅡ,Page2495-2498.Reference to a book:
[8]W.Qiang,Mine water prevention and cure pro-vides interpretation,page 4.

